SemiBin Subcommand Reference
See the usage page for a more readable overview of how SemiBin can be used. This page exhaustively lists all the subcommands and their options.
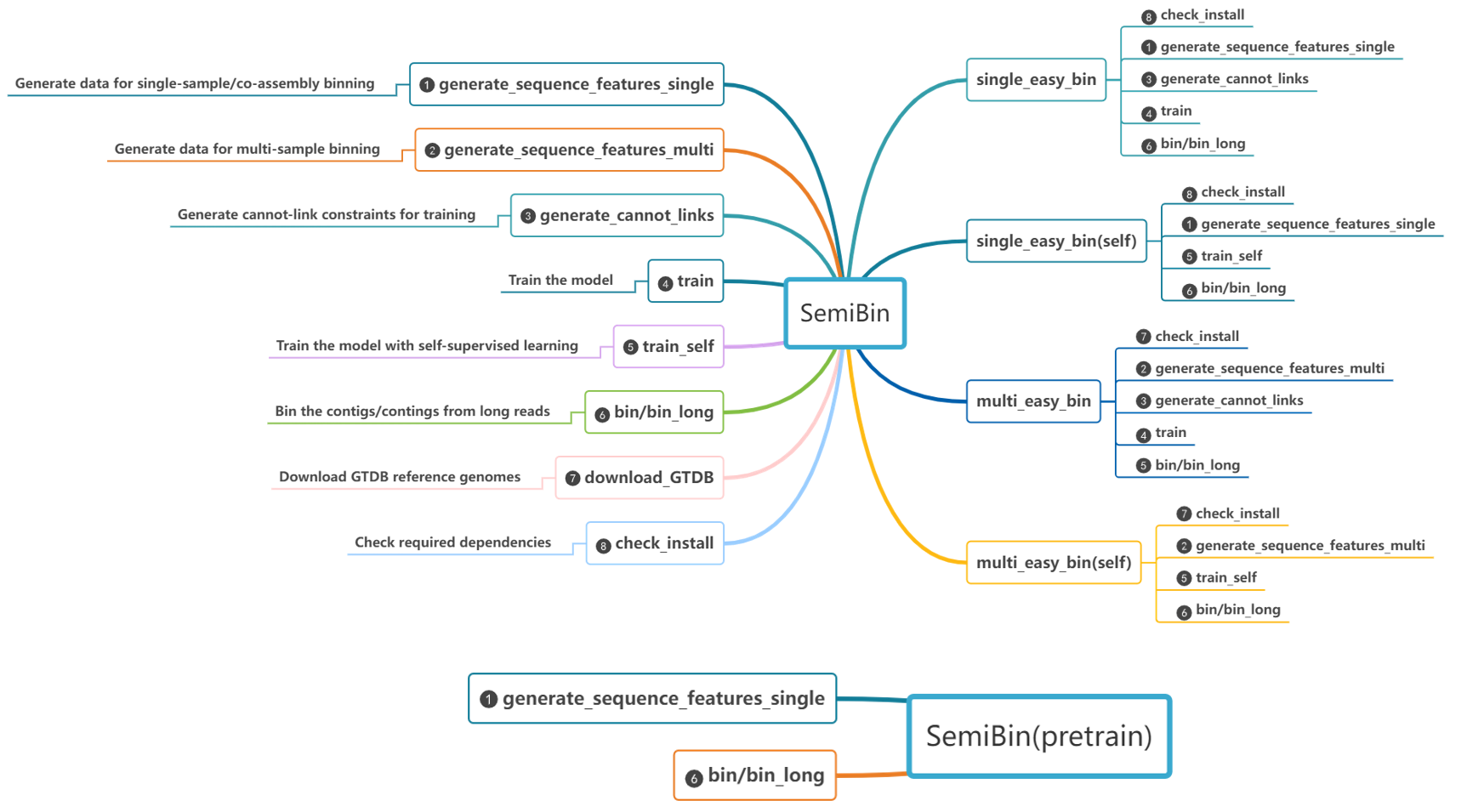
SemiBin works using a subcommand interface.
Most uses are covered by either the single_easy_bin or multi_easy_bin subcommands, but you can use the other subcommands for more control.
single_easy_bin
Reconstruct bins with single or co-assembly binning using one command.
single_easy_bin requires the contig file (assembly from reads), BAM files (reads mapping to the contig) as inputs and outputs reconstructed bins in the output_recluster_bins directory (see [how to generate inputs for SemiBin] and [usage] for more information).
Required arguments
-i/--input-fasta: Path to the input contig fasta file (gzipandbzip2compression are accepted).-b/--input-bam: Path to the input BAM (.bamextension) or CRAM (.cram) files. You can pass multiple BAM files, one per sample.-o/--output: Output directory (will be created if non-existent).-a/--abundancePath to the abundance file from strobealign-aemb. This can only be used when samples used in binning above or equal 5.
Recommended arguments
If your data comes from one of the habitats for which we have a prebuilt model, using the --environment argument will use it instead of training a new model.
--environment: Environment for the built-in model (human_gut/dog_gut/ocean/soil/cat_gut/human_oral/mouse_gut/pig_gut/built_environment/wastewater/chicken_caecum/global).
If --environment is not given, a new model is learned, which is computationally intensive.
- [SemiBin 1.4 and above]
--self-supervisedor--semi-supervised: specify the training algorithm used - [SemiBin 1.3]
--training-type: Training algorithm used to train the model (semi/self). This is still accepted for backwards compatibility, but deprecated.
The original manuscript describing SemiBin1 presents the semi-supervised approach. Starting in version 1.3, self-supervised learning is also supported, which should be an improvement in both results and computational resource usage.
- [SemiBin 1.4 and above]
--sequencing-type=short_reads/--sequencing-type=long_reads
Optional arguments to control output
--compression: Whether to compress outputs to save space. Should be one ofnone(default if usingSemiBin) /gz(default if usingSemiBin2) /xz/bz2.--tag-output: If passed an argument (e.g.,--tag-output=mysample), then output bin files will include the tag. This can help distinguish results from multiple runs.
Optional arguments to control computational resource usage
-p/--processes/-t/--threads: Number of CPUs used (0, the default, indicates that all CPUs should be used).--write-pre-reclustering-bins/--no-write-pre-reclustering-bins: Whether to write pre-reclustering bins (defaults to true in SemiBin1; and false in SemiBin2).--engine: device used to train the model (auto/gpu/cpu);auto(default) means that SemiBin with attempt to detect and use GPU and fallback to CPU if no GPU is found.--tmpdir: set temporary directory.-r/--reference-db-data-dir: GTDB reference directory (Default:$HOME/.cache/SemiBin/mmseqs2-GTDB). This is only useful if you are using the deprecated semi-supervised mode). In that case, SemiBin will lazily download GTDB if it is not found there. Note that a lot of disk space is used.
Optional arguments to set internal parameters
--random-seed: Random seed to reproduce results.--orf-finder: gene predictor used to estimate the number of bins. Must be one ofprodigal(default sincev0.7),fast-naive(available sincev1.5, this is a very fast internal implementation, default if usingSemiBin2), orfraggenescan(which is faster thanprodigal, but cannot be installed in all platforms and is still not as fast as thefast-naivemethod).
Optional arguments to bypass internal steps
Several internal steps can be bypassed if you wish to compute it outside of SemiBin. For example, calling mmseqs2 for contig annotation takes a lot of time and if you perform it for your dataset independently of SemiBin, you can reuse the results here and avoid recomputation.
These should be considered advanced uses as passing wrongly formatted files can easily lead to suboptimal or non-sensical results.
--taxonomy-annotation-table: TAXONOMY_TSV, Pre-computed mmseqs2 format taxonomy TSV file to bypass mmseqs2 GTDB annotation. When running with multi-sample binning, please make sure that the order of the taxonomy TSV file and the contig file (used for the combined fasta) is same.--depth-metabat2: depth file generated by metabat2 (only used with single-sample binning).--prodigal-output-faa: predicted protein coding genes from the contigs used for binning. The important element is that predicted protein coding genes must be named following the format{contig}_{index}where{contig}is the contig name and{index}is some ORF identifier, separated by a single underscore. Prodigal uses this format, but not all tools do.
Optional arguments to set internal parameters (advanced)
Generally speaking, you should use the default values for all these parameters, but they are provided if you want to tune the algorithms. If you find that changing these significantly improves the results of binning, we would appreciate if you got in touch.
--minfasta-kbs: minimum bin size in kilo-basepairs (Default: 200).--no-recluster: Do not recluster bins. This saves a small amount of time, but pre-reclustering bins are always output.--epochs: Number of epochs used in the training process (Default: 15).--batch-size: Batch size used in the training process (Default: 2048).--max-node: Percentage of contigs that considered to be binned (Default: 1).--max-edges: The maximum number of edges that can be connected to one contig (Default: 200).--ratio: If the ratio of the number of base pairs of contigs between 1000-2500 bp smaller than this value, the minimal length will be set as 1000bp, otherwise 2500bp. If you set -m parameter, you do not need to use this parameter. If you use SemiBin with multi steps and you use this parameter, please use this parameter consistently with all subcommands (Default: 0.05).-m/--min-len: Minimal length for contigs in binning. If you use SemiBin with multi steps and you use this parameter, please use this parameter consistently with all subcommands. (Default: SemiBin chooses 1000bp or 2500bp according the ratio of the number of base pairs of contigs between 1000-2500 bp).--ml-threshold: Length threshold for generating must-link constraints. By default, the threshold is calculated from the contigs, and the default minimum value is 4,000 bp.--cannot-name:Name for the cannot-link file (Default:cannot).
multi_easy_bin
Reconstruct bins with multi-samples binning using one-line command.
The command multi_easy_bin requires the combined contig file from several samples, BAM files (reads mapping to the combined contig) as inputs and outputs the reconstructed bins in the samples/[sample]/output_recluster_bins directory.
Required arguments
-b/--input-bam: Path to the input BAM (.bam) or CRAM (.cram) files. You can pass multiple BAM files, one per sample.--input-fastaand--outputare same as forsingle_easy_bin.
Optional arguments
-s/--separator: Used when multiple samples binning to separate sample name and contig name (Default is:).- [SemiBin 1.4 and above]
--self-supervisedor--semi-supervised: specify the training algorithm used - [SemiBin 1.3]
--training-type: Training algorithm used to train the model (semi/self). This is still accepted for backwards compatibility, but deprecated. --reference-db-data-dir,--processes,--minfasta-kbs,--recluster,--epochs,--batch-size,--max-node,--max-edges,--random-seed,--ratio,--min-len,--ml-threshold,--no-recluster,--orf-finder,--engineand--tmpdirare same as forsingle_easy_bin
generate_cannot_links
:::{warning} This is only useful for using the older (deprecated) semi-supervised approach :::
Run the contig annotations using mmseqs with GTDB and generate cannot-link file used in the semi-supervised deep learning model training.
The subcommand generate_cannot_links requires the contig file as inputs and outputs the cannot-link constraints.
Required arguments
--input-fasta--output
These are the are same as for single_easy_bin.
Optional arguments
--cannot-name-r/--reference-db-data-dir--ratio--min-len--ml-threshold--taxonomy-annotation-table--tmpdir-a/--abundance
These are the are same as for single_easy_bin.
generate_sequence_features_single
The subcommand generate_sequence_features_single requires the contig file and BAM file(s) as inputs and generates training data (data.csv; data_split.csv) for single and co-assembly binning.
Required arguments
-i/--input-fasta-b/--input-bam-o/--output-a/--abundance
These are the are same as for single_easy_bin.
Optional arguments
-p/--processes/-t/--threads--ratio--min-len--ml-threshold--depth-metabat2--tmpdir
These are same as for single_easy_bin.
generate_sequence_features_multi
The subcommand generate_sequence_features_multi requires the combined contig file and BAM files as inputs and generates training data (data.csv and data_split.csv files) for multi-sample binning.
Required arguments
-i/--input-fasta-o/--output-b/--input-bam-a/--abundance
These are the same as for multi_easy_bin.
Optional arguments
-p/--processes/-t/--threads,--ratio,--min-len,--ml-thresholdand--tmpdirare the same as forsingle_easy_bin.-s/--separatorare the same as formulti_easy_bin.
train (train_semi in SemiBin2)
The train (train_semi in SemiBin2) subcommand requires the contig file and outputs from the generate_sequence_features_single, generate_sequence_features_multi and generate_cannot_links subcommand as inputs (data.csv, data_split.csv and cannot.txt) and outputs the trained model.
Note that you can train a model from multiple samples for use in single sample binning!
Required arguments
-i/--input-fasta(same as forsingle_easy_bin)-o/--output(same as forsingle_easy_bin)--data: Path to the inputdata.csvfile (typically generated by a previous call togenerate_sequence_features_singleorgenerate_sequence_features_multi).--data_split: Path to the inputdata_split.csvfile.-c/--cannot-link: Path to the input cannot link file generated from other additional biological information, one row for each cannot link constraint. The file format is comma separated:contig_1,contig_2.- [SemiBin 1.4 and above]
--train-from-many: When passed, train models from many samples (training across several samples can result in a better pre-trained model for single-sample binning). When this flag is used, you must passdata,data_split,cannot, andfastafiles for corresponding sample in the exact same order. Note: You can only use this option when single-sample binning. Training from many samples with multi-sample binning is not supported (see [training] for more information). - [Before SemiBin 1.4]
--mode: [single/several] Prior to SemiBin 1.4, using--mode=severalwas used for the same purpose as using--train-from-many. This option is still accepted for backwards compatibility, but is deprecated.
Optional arguments
--epochs--batch-size-p/--processes/-t/--threads--random-seed--ratio--min-len--orf-finder--engine
These have the same meaning as for single_easy_bin
train_self
The train_self subcommand requires the contig file and outputs from the generate_sequence_features_single, generate_sequence_features_multi subcommand as inputs (data.csv, data_split.csv) and outputs the trained model with a self-supervised way.
Required arguments
-o/--output(same as forsingle_easy_bin)--data: Path to the inputdata.csvfile (typically generated by a previous call togenerate_sequence_features_singleorgenerate_sequence_features_multi).--data_split: Path to the inputdata_split.csvfile.- [SemiBin 1.4 and above]
--train-from-many: When passed, train models from many samples (training across several samples can result in a better pre-trained model for single-sample binning). When this flag is used, you must passdata,data_split, andfastafiles for corresponding sample with same order. Note: You can only use this option when single-sample binning. Training from many samples with multi-sample binning is not supported (see [training] for more information). - [Before SemiBin 1.4]
--mode: [single/several] Prior to SemiBin 1.4, using--mode=severalwas used for the same purpose as using--train-from-many. This option is still accepted for backwards compatibility, but is deprecated.
Optional arguments
--epochs--batch-size-p/--processes/-t/--threads--random-seed--engine
These have the same meaning as for single_easy_bin
bin_short
The bin_short subcommand (for backwards compatibility reasons, bin is accepted as an alias) requires the contig file and output (files data.csv, model.h5) from the generate_sequence_features_single, generate_sequence_features_multi and train subcommand as inputs and output the final bins in the output_recluster_bins directory.
Required arguments
--data(same as fortrain)i/--input-fasta(same as forsingle_easy_bin)-o/--output(same as forsingle_easy_bin)
Also, one of the following two arguments is required:
--environment: Which pre-trained model to use (seesingle_easy_bin)--model: Path to the trained model
See [training] for more information on how models can be generated.
Optional arguments
--minfasta-kbs,--recluster,--max-node,--max-edges,-p/--processes/-t/--threads,--random-seed,--environment,--ratio,--min-len,--no-recluster,--orf-finder,--engineand--depth-metabat2are the same as forsingle_easy_bin
bin_long
The bin_long subcommand requires the contig file and output (files data.csv, model.h5) from the generate_sequence_features_single, generate_sequence_features_multi and train subcommand as inputs and output the final bins in the output_bins directory.
Required arguments
--data(same as fortrain)i/--input-fasta(same as forsingle_easy_bin)-o/--output(same as forsingle_easy_bin)
Also, one of the following two arguments is required:
--environment: Which pre-trained model to use (seesingle_easy_bin)--model: Path to the trained model
See [training] for more information on how models can be generated.
Optional arguments
--minfasta-kbs,-p/--processes/-t/--threads,--random-seed,--environment,--ratio,--min-len,--orf-finder,--engineand--depth-metabat2are the same as forsingle_easy_bin
download_GTDB
Download reference genomes (GTDB). This is used for semi-supervised learning when learning a new model.
-r/--reference-db-data-dir: Where to store the GTDB data (default:$HOME/.cache/SemiBin/mmseqs2-GTDB)-f/--force: Whether to download GTDB even if the data is found at the path (default is to not download).
If you download GTDB to a different directory than the default, you should then pass that path to every command (-r) to ensure that it is found.
check_install
Checks whether required dependencies are available (useful for trouble-shooting).
Optional argument
--allow-missing-mmseqs2[since SemiBin 1.4]: When used, failure to findmmseqswill not lead to an error.
concatenate_fasta
Concatenate fasta files for multi-sample binning.
The contigs are renamed to include the sample name followed by a separator character.
The separator character cannot occur in any of your samples, so if any sample contains the default separator (:), you must change it and pass that information to every command (using the --separator/-s argument).
Required arguments
-i/--input-fasta(same as forsingle_easy_bin)-o/--output(same as forsingle_easy_bin)
Optional arguments
-s/--separatoris the same as themulti_easy_bin(see comment above).-m: Discard sequences below this length (default:0).--compression(since version1.6): whether to compress the output (defaults togzif usingSemiBin2)
citation
Available since version 2.1
Prints citation
Optional argument
--bibtex: Use BibTeX format--ris: Use RIS format (for Endnote and other tools)--chicago: Use Chicago format (default)