SemiBin
If you use this software in a publication please cite:
Pan, S., Zhu, C., Zhao, XM. et al. A deep siamese neural network improves metagenome-assembled genomes in microbiome datasets across different environments. Nat Commun 13, 2326 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29843-y
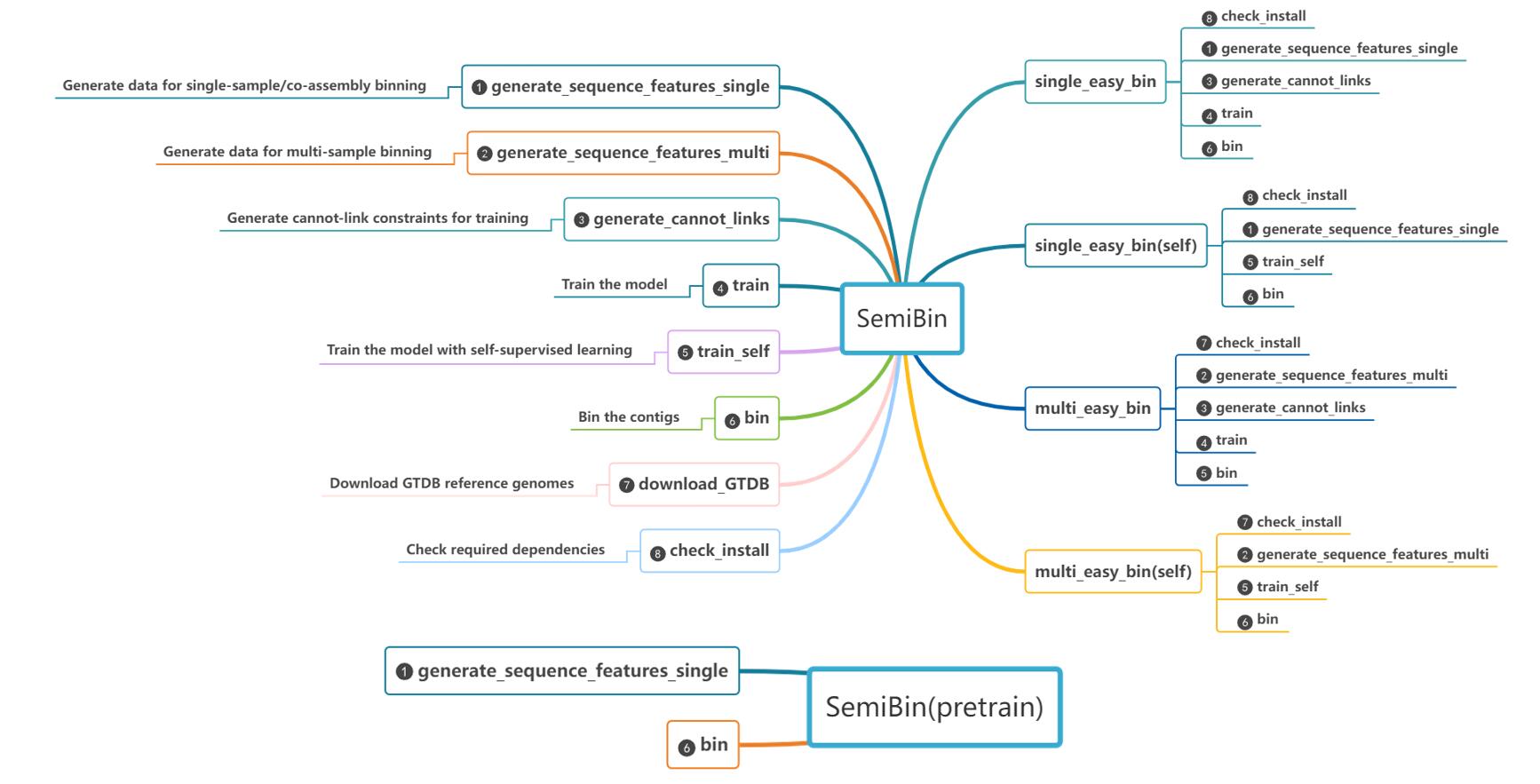
SemiBin is a command line tool for metagenomic binning with semi-supervised siamese neural network using additional information from reference genomes and contigs themselves. It supports single sample, co-assembly, and multi-samples binning modes.
Install
The simplest way to install is to use conda.
conda create -n SemiBin
conda activate SemiBin
conda install -c conda-forge -c bioconda semibin
See Install for how to install from source or how to enable GPU usage.
SemiBin Examples
See the usage page for a more in-depth overview of how SemiBin can be used.
Single-sample binning
[How to generate inputs to SemiBin]
If your assembled contigs are in a file called S1.fa (contig file in FASTA format) and you mapped reads and sorted the output to generate the BAM file S1.sorted.bam, then you there are two options.
1. Using a pre-trained model. This is the fastest option and should work the best if you have metagenomes from one of our prebuilt habitats (alternatively, you can use the global "habitat" which combines all of them).
SemiBin single_easy_bin \
--environment human_gut \
-i S1.fa \
-b S1.sorted.bam \
-o output
2. Learn a new model. Alternatively, you can learn a new model for your data. The main disadvantage is that this approach will take a lot more time and use a lot more memory. While using a pre-trained model should take a few minutes and use 4-6GB of RAM, training a new model may take several hours and use 40GB of RAM.
SemiBin single_easy_bin \
--environment human_gut \
-i S1.fa \
-b S1.sorted.bam \
-o output